Machines
Definitions in English
A Machine is a device that directs and controls energy, often in the form of movement or electricity, to produce a certain effect.
A computer is a type of machine and so is a robot, car, bicycle, drone or an autonomous system.
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to automatically carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs, which enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system
- includes the hardware, operating system, software, and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation;
- or to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster,
- whose newest manifestation is cloud computing.
- Cloud computing is "a paradigm for enabling network access to a scalable and elastic pool of shareable physical or virtual resources with self-service provisioning and administration on-demand," according to ISO.
Computer Architecture 
- von Neumann Architecture gives the model of a computer with a central processing unit (CPU), memory unit and I/O devices (right)
Computer Hardware
Computer hardware includes the physical parts of a computer, such as the central processing unit (CPU), random-access memory (RAM), motherboard, computer data storage, graphics card, sound card, and computer case. It includes external devices such as a monitor, mouse, keyboard, and speakers.
Central Processing Unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary processor in a given computer.
Computer Memory
Computer memory stores information, such as data and programs, for immediate use in the computer.
Multi-Core Processor
A multi-core processor (MCP) is a microprocessor on a single integrated circuit (IC) with two or more separate central processing units (CPUs), called cores to emphasize their multiplicity (for example, dual-core or quad-core).
Graphics Processing Unit
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed for digital image processing... GPUs were later found to be useful for non-graphic calculations involving embarrassingly parallel problems due to their parallel structure. The ability of GPUs to rapidly perform vast numbers of calculations has led to their adoption in diverse fields including artificial intelligence (AI) where they excel at handling data-intensive and computationally demanding tasks.
Computer Software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the execution of a computer.
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
Android, iOS, and iPadOS are mobile operating systems, while Microsoft Windows, macOS, and Linux are desktop operating systems. Linux distributions are dominant in the server and supercomputing sectors.
HarmonyOS (HMOS) (Chinese: 鸿蒙; pinyin: Hóngméng; trans. "Vast Mist") is a distributed operating system developed by Huawei for smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, smart watches, personal computers and other smart devices.
IP, Copyright & License 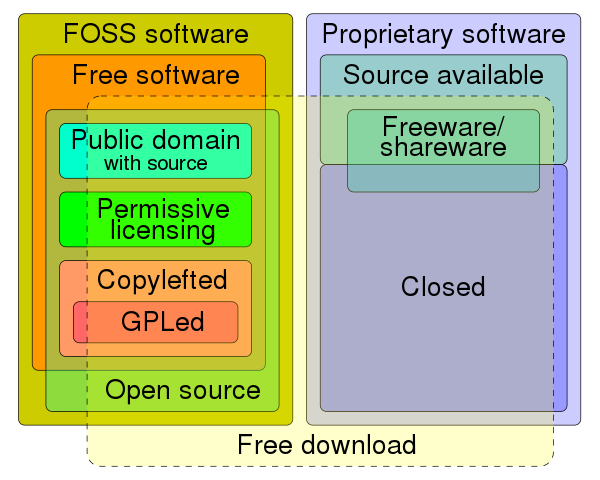
- Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect.
- A copyright is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the exclusive legal right to copy, distribute, adapt, display, and perform a creative work, usually for a limited time.
- Software copyright is the application of copyright in law to machine-readable software.
- A software license is a legal instrument governing the use or redistribution of software.
Linux, GPL and Distros
Linux (/ˈlɪnʊks/ LIN-uuks) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Benedict Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries—most of which are provided by third parties—to create a complete operating system, designed as a clone of Unix and released under the copyleft GPL license.
We will use Ubuntu and Alpine Linux distros in docker containers.
Dive Deeper: Linux
Linux distributions are dominant in the server and supercomputing sectors.


Cluster Computing
A computer cluster is a set of computers that work together so that they can be viewed as a single system.
Cloud Computing
The newest manifestation of cluster computing is cloud computing.
Service Models
Cloud Computing Vendors
Vendor Lock-In
Anatomy of an AI System
The Amazon Echo as an anatomical map of human labor, data and planetary resources, by Kate Crawford and Vladan Joler
Exercise
- Deep Dive into Amazon Echo by reading https://anatomyof.ai/ ~1h